Monday, 27 June 2016
Wednesday, 22 June 2016
Saturday, 18 June 2016
Useful Data for Site Execution (Construction Site) Part-3
Slipform construction is a method for building large towers or bridges from concrete. The name refers to the moving form the concrete is poured into, which moves along the project as the previously poured concrete hardens behind it. The technique has also been applied to road construction.
Vertical Slipform relies on the quick-setting properties of concrete requiring a balance between early strength gain and workability. Concrete needs to be workable enough to be placed to the formwork and strong enough to develop early strength so that the form can slip upwards without any disturbance to the freshly placed concrete.
From foundation to rooftop of even the very tallest projects, with the system’s hydraulic jacks, installing steel reinforcement and pouring concrete become much easier and faster, plus can be more efficiently controlled to assure the highest quality finished cement structure.
SLIPFORM technology virtually eliminates unnecessary waste and hazards, making this construction system even more efficient and economical.
SLIPFORM technology virtually eliminates unnecessary waste and hazards, making this construction system even more efficient and economical.
Friday, 17 June 2016
Useful Data for Site Execution (Construction Site) Part-2
Following are few general points to remember for civil site engineers to make the construction work easier while maintaining quality of construction.
- Lapping is not allowed for the bars having diameters more than 36 mm.
- Chair spacing maximum spacing is 1.00 m (or) 1 No per 1m2.
- For dowels rod minimum of 12 mm diameter should be used.
- Chairs minimum of 12 mm diameter bars to be used.
- Longitudinal reinforcement not less than 0.8% and more than 6% of gross C/S.
- Minimum bars for square column is 4 No’s and 6 No’s for circular column.
- Main bars in the slabs shall not be less than 8 mm (HYSD) or 10 mm (Plain bars) and the distributors not less than 8 mm and not more than 1/8 of slab thickness.
- Minimum thickness of slab is 125 mm.
- Dimension tolerance for cubes + 2 mm.
- Free fall of concrete is allowed maximum to 1.50m.
- Lap slices not be used for bar larger than 36 mm.
- Water absorption of bricks should not be more than 15 %.
- PH value of the water should not be less than 6.
- Compressive strength of Bricks is 3.5 N / mm2.
- In steel reinforcement binding wire required is 8 kg per MT.
- In soil filling as per IS code, 3 samples should be taken for core cutting test for every 100m2.
Density of Materials:
Material
|
Density
|
Bricks
|
1600 – 1920 kg/m3
|
Concrete block
|
1920 kg/ m3
|
Reinforced concrete
|
2310 – 2700 kg/ m3
|
Curing time of RCC Members for different types of cement:
Super Sulphate cement: 7 days
Ordinary Portland cement OPC: 10 days
Minerals & Admixture added cement: 14 days
De-Shuttering time of different RCC Members
RCC Member
|
De-shuttering time
|
For columns, walls, vertical form works
|
16-24 hrs.
|
Soffit formwork to slabs
|
3 days (props to be refixed after removal)
|
Soffit to beams props
|
7 days (props to refixed after removal)
|
Beams spanning upto 4.5m
|
7 days
|
Beams spanning over 4.5m
|
14 days
|
Arches spanning up to 6m
|
14 days
|
Arches spanning over 6m
|
21 days
|
Cube samples required for different quantity of concrete:
Quantity of Concrete
|
No. of cubes required
|
1 – 5 m3
|
1 No’s
|
6 0 15 m3
|
2 No’s
|
16 – 30 m3
|
3 No’s
|
31 – 50 m3
|
4 No’s
|
Above 50 m3
|
4 + 1 No’s of addition of each 50 m3
|
Monday, 13 June 2016
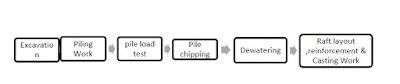
Useful Data for Site Execution (Construction Site) Part-1 Incl. Types of Equipment use on site and Column layout-Casting
Site soil Excavation & Foundation:-
Prior to start of construction
work excavation is done at site up to the level required for start
of construction. To provide
access to vehicles construction machineries Ramp is made with
proper slope.
Poclain
used for excavation
Dozer
used for making Ramp, dumping & spreading soil
Slope stabilization is done of cutting soil edges by keeping
sand bags at slopes & by
Step cutting so that soil doesn’t collapse during construction
stage causing safety Issue.
Proper drainage arrangement is done to avoid water logging.
Land around the construction area is levelled for keeping
construction material & Machinery
Tower Boom(Placer Boom)
Boom is
fixed in the tower in position from where it is easy to whole area of tower is
accessible.
· Can pump
upto 50 cum/hr. or Depends upon its Power.
Hydra machine used for column reinforcement Shifting
Used
for excavation where quantity of soil to be excavated is less
Can
also used for various other construction purposes like shifting of material,
ground
dressing
& levelling.
Structural
Member Construction Methodology &
specifications
1. Column
Columns are
compressive member of a structure. There position in a structure should be such
that, they carry the load coming efficiently.
Activities involve in Column
construction
ü Column Layout
After casting of raft again the layout of column is
done in order to check the actual position of
Vertical bars of columns. The layout is also helpful
to place the shuttering on actual position, so that
the column should be in proper position according to
drawing(Column layout drawing). Column
Layout is doe according to the Grid line mentioned
in coordinated framing plan. Grid line is marked
Near the column as per drawing.
Ø Why Column Layout??
Ø So that column remains in their position decided as
per Co-ordinate drawing of Tower.
Ø Verticality of structure is maintained.
Ø So that area of particular Flat doesn’t reduce due
to dislocation of column from actual
Assign position.
ü Bar Binding Work :
Steel Grade Used: FE 500D
Dia of bar used : 12mm to 32mm
for longitudinal bars & 8mm to 10mm for Tie bars.
Tie bar hooks are bend up at 45ᵒ
as per IS 456
Coupler/Reducer: vertical joints in case of longitudinal bars of column are provide
using
coupler. Where ever Dia of column is reducing in above floor reducer
is used to provide
joins
· Used for Bars of Dia 16mm to 32mm
· Lap length of 36D is provide in case of
12mm Dia bar or bar reducing from 16mm to
12mm.
· Thread are provide at ends of bar for
couple/reducer.
Coupler used for joining vertical bar in column.
Couplers
Bar binding of column
Important
points For bar binding Of columns :-
· Lap Zone is
H/3 from top & bottom slab.
· Alternate
longitudinal Bar of column should have a length difference of 600mm so that
vertical
reinforcement joint doesn’t come at 1 point as shear concentration point of
view.
· Coupler
should be properly tightened
a. Formwork for
columns
The shuttering either conventional or system is
fixed around column and plumb of this shuttering
is checked out. At bottom the T shaped bars keeps
the shuttering on position and at top and
middle cover blocks are fixed so that proper cover
could be provide to reinforcement. The T
shaped bar at bottom and cover blocks at middle and
top ensure the straightness of vertical
Reinforcement.
Table: Period of removal of formwork
S. No.
|
Description of structural member
|
Period of time
|
1
|
Walls, columns and vertical sides of beams
|
16-24 Hours
|
It should be strong enough to withstand all types of dead and live loads.A good formwork should satisfy the following requirements:
- It should be rigidly constructed and efficiently propped and braced both horizontally and vertically, so as to retain its shape.
- The joints in the formwork should be tight against leakage of cement grout.
- Construction of formwork should permit removal of various parts in desired sequences without damage to the concrete.
- The material of the formwork should be cheap, easily available and should be suitable for reuse.
- The formwork should be set accurately to the desired line and levels should have plane surface.
- It should be as light as possible.
- The material of the formwork should not warp or get distorted when exposed to the elements.
- It should rest on firm base.
Types of Formwork (Shuttering) for Concrete Construction:
Timber Formwork:
Timber for formwork should satisfy the following requirement:
It should be
- well seasoned
- light in weight
- easily workable with nails without splitting
- free from loose knots
Timber used for shuttering for exposed concrete work should have smooth and even surface on all faces which come in contact with concrete.
Normal sizes of members for timber formwork:
Sheeting for slabs, beam, column side and beam bottom
|
25 mm to 40mm thick
|
Joints, ledges
|
50 x 70 mm to 50 x 150 mm
|
Posts
|
75 x 100mm to 100 x 100 mm
|
Resin bonded plywood sheets are attached to timber frames to make up panels of required sizes. The cost of plywood formwork compares favourably with that of timber shuttering and it may even prove cheaper in certain cases in view of the following considerations:
Plywood Formwork
- It is possible to have smooth finish in which case on cost in surface finishing is there.
- By use of large size panels it is possible to effect saving in the labour cost of fixing and dismantling.
- Number of reuses are more as compared with timber shuttering. For estimation purpose, number of reuses can be taken as 20 to 25.
Steel Formwork
This consist of panels fabricated out of thin steel plates stiffened along the edges by small steel angles. The panel units can be held together through the use of suitable clamps or bolts and nuts. The panels can be fabricated in large number in any desired modular shape or size. Steel forms are largely used in large projects or in situation where large number reuses of the shuttering is possible. This type of shuttering is considered most suitable for circular or curved structures.
Steel forms compared with timber formwork:
- Steel forms are stronger, durable and have longer life than timber formwork and their reuses are more in number.
- Steel forms can be installed and dismantled with greater ease and speed.
- The quality of exposed concrete surface by using steel forms is good and such surfaces need no further treatment.
- Steel formwork does not absorb moisture from concrete.
- Steel formwork does not shrink or warp.
Construction of Concrete formwork:
This normally involves the following operations:
- Propping and centring
- Shuttering
- Provision of camber
- Cleaning and surface treatment
Order and method of removing formwork:
The sequence of orders and method of removal of formwork are as follows:
- Shuttering forming the vertical faces of walls, beams and column sides should be removed first as they bear no load but only retain the concrete.
- Shuttering forming soffit of slabs should be removed next.
- Shuttering forming soffit of beams, girders or other heavily loaded shuttering should be removed in the end.
Rapid hardening cement, warm weather and light loading conditions allow early removal of formwork. The formwork should under no circumstances be allowed to be removed until all the concrete reaches strength of atleast twice the stresses to which the concrete may be subjected at the time of removal of formwork. All formworks should be eased gradually and carefully in order to prevent the load being suddenly transferred to concrete.
Conventional column shuttering
b. Casting of
columns
After ensuring the verticality and correct position
of column’s shuttering the columns are casted .
· Plumb
is again checked after the casting as column shuttering displace a little by
pouring
Concrete pressure
· Grade
of concrete.
· Nominal
cover provided: 40mm
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)